
This is an important consideration for distributed systems.Ī particular generation size makes a trade-off between these four metrics.
Promptness is the time between when an object becomes dead, and when the memory becomes available. Footprint is the working size of the JVM process, measured in pages and cache lines. Two other considerations are footprint and promptness. Pauses are times when an application appears unresponsive due to GC. Throughput is the percentage of the total time spent on other activities apart from GC. The two primary measures of garbage collection performance are throughput and pauses. Consider pooling only if object construction cost is high and significantly affects execution profiles. So, custom object pooling is not often required. When the old generation fills up, it triggers a major collection which involves the entire object heap.īoth HotSpot and Solaris JDK use thread local object allocation pools for lock-free, fast, and scalable object allocation. When the new generation fills up, it triggers a minor collection in which the surviving objects are moved to the old generation. This process comes with an overhead and is not required for enterprise web applications. This provides a high probability of small pauses.
JAVA CONTROL PANEL MAX HEAP SIZE FULL
They divide the full GC into several incremental pieces.

Other GC algorithms, such as the Concurrent Mark Sweep (CMS) algorithm, are incremental. The frequent young space collections are quick (a few milliseconds), while the full generation collection takes a longer (tens of milliseconds to a few seconds, depending upon the heap size). Collecting the tenured space is also referred to as doing a full generation collection. So, it is garbage collected less frequently and each collection takes longer than a young space only collection. The tenured generation is larger and fills up less quickly. Objects that survive multiple young space collections are tenured, meaning they are copied to the tenured generation. The young generation uses a fast copying garbage collector which employs two semi-spaces (survivor spaces) in the eden, copying surviving objects from one survivor space to the second. The JVM allocates new objects in the eden space, and moves longer lived objects from the new generation to the old generation. The new generation includes the new object space (eden), and two survivor spaces. The heap space is divided into the old and the new generation. As these objects accumulate, a low memory condition occurs forcing GC to take place. The efficiency of a generational memory system is based on the observation that most of the objects are short lived.
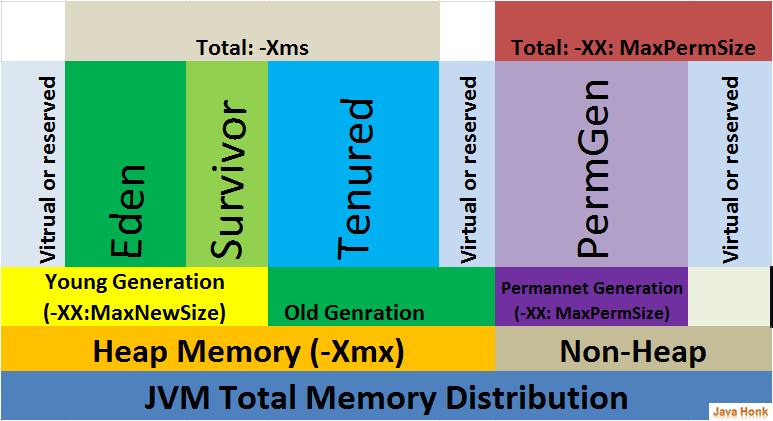
A generational memory system divides the heap into a few carefully sized partitions called generations. The process of locating and removing the dead objects can stall any application and consume as much as 25 percent throughput.Īlmost all Java Runtime Environments come with a generational object memory system and sophisticated GC algorithms. Garbage collection (GC) reclaims the heap space previously allocated to objects no longer needed. Refer to the online help for complete information about the settings on this page.įor more information on server-class machine detection in Java SE 6.0, see Server-Class Machine Detection.įor more information on JVMs, see Java Virtual Machines. If using the Administration Console, navigate to the Configurations> configuration-name>JVM Settings node, and then click the JVM Options tab. You can override the default JVM options by following the instructions in " Administering JVM Options" in Oracle GlassFish Server Administration Guide. Invoke it by using the -server JVM command-line option.īy default, the GlassFish Server uses the JVM setting appropriate to the purpose:ĭeveloper Profile, targeted at application developers, uses the -client JVM flag to optimize startup performance and conserve memory resources.Įnterprise Profile, targeted at production deployments, uses the -server JVM flag to maximize program execution speed.

The server VM is designed for maximum program execution speed. Invoke it by using the -client JVM command-line option. The client VM is tuned for reducing startup time and memory footprint. Java SE 6.0 provides two implementations of the HotSpot Java virtual machine (JVM):


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
